Hair loss is a big worry for many men. It can hurt their self-esteem and confidence. Many things can cause it, like genetics, changes in hormones, and how we live.
The hair growth cycle is very complex. Knowing how it works can help men deal with hair loss. Things like getting older, health issues, and our lifestyle choices can affect hair growth. This can lead to hair loss.
Key Takeaways
- Genetics play a significant role in hair loss among men.
- Hormonal changes can contribute to hair loss.
- Lifestyle factors, such as diet and stress, can impact hair growth.
- Understanding the hair growth cycle is key to fighting hair loss.
- Age and health problems can also cause hair loss.
Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
To understand hair loss, we must first know the hair growth cycle. This cycle has several phases. Knowing these phases helps us see how hair loss happens in men.
The Four Phases of Hair Growth
The hair growth cycle has four main phases: anagen, catagen, telogen, and exogen. The anagen phase is when hair grows fast. It can last from 2 to 6 years.
The catagen phase is short, lasting 2-3 weeks. During this time, the hair follicle shrinks and detaches. The telogen phase is the resting phase, lasting about 3 months. Here, the hair is released and falls out. The exogen phase is when the hair is shed from the follicle.
| Phase | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Anagen | Active growth phase | 2-6 years |
| Catagen | Transitional phase | 2-3 weeks |
| Telogen | Resting phase | 3 months |
| Exogen | Shedding phase | Varies |
Normal Hair Shedding vs. Hair Loss
It’s normal to lose some hair daily. But excessive hair shedding or loss means there might be a problem. Knowing the difference is key to spotting issues early.
How Hair Follicles Function
Hair follicles are key to hair growth. Each follicle goes through growth, rest, and shedding phases. The health of these follicles affects hair density and growth.

Understanding the hair growth cycle and follicle function helps us understand hair loss in men. This knowledge can lead to finding solutions.
What Causes Hair Loss in Men: The Main Culprits
Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the top reason for hair loss in men. It’s caused by genetics and hormones. This condition shows up as a receding hairline or thinning at the crown.
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
Male pattern baldness affects many men around the world. It’s linked to genetics and hormones, like testosterone turning into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a strong form of testosterone that plays a big part in male pattern baldness.

DHT and Its Role in Hair Loss
DHT causes hair loss by attaching to androgen receptors in hair follicles. This makes the follicles shrink and the hair growth cycle shorter. As a result, hairs become thinner and shorter, eventually stopping growth.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal issues, like too much testosterone and DHT, are major causes of hair loss in men. Other hormonal problems, like thyroid issues, can also lead to hair loss, but they’re less common.
| Hormone | Role in Hair Loss |
|---|---|
| Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) | Primary contributor to androgenetic alopecia, causing follicle shrinkage |
| Testosterone | Precursor to DHT; high levels can contribute to hair loss |
| Thyroid Hormones | Imbalances can lead to hair loss, though less common |
Knowing about genetics, DHT, and hormonal imbalances is key to fighting hair loss in men. By understanding these causes, people can find better treatments and slow down hair loss.
Genetic Factors in Male Hair Loss
Hair loss in men often comes from their genes. This is called androgenetic alopecia or male pattern baldness. It happens because hair follicles are sensitive to DHT, a form of testosterone.
The Hereditary Component
Studies show that men with a family history of baldness are more likely to lose their hair. The hereditary part is complex, with many genes affecting how hair follicles react to androgens.

Maternal vs. Paternal Inheritance Myths
Many think baldness comes only from the mother. But, both parents contribute to the risk. The X chromosome from the mother can influence baldness, but the father’s genes also matter.
Genetic Testing for Hair Loss Predisposition
Genetic testing can now spot the risk of male pattern baldness. It can show an individual’s risk and help with early prevention or treatment.
| Genetic Factor | Influence on Hair Loss |
|---|---|
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Sensitivity to DHT |
| Maternal Inheritance | X chromosome genes |
| Paternal Inheritance | Multiple genes |
Knowing about genetic hair loss can help men protect their hair. While genes are key, lifestyle and environment also play a part in hair loss.
Age-Related Hair Loss in Men
Age is a big risk for hair loss in men. The chance of losing hair grows as they get older. This natural process is influenced by many factors, like changes in hair follicles and health.

How Age Affects Hair Follicles
As men age, their hair follicles change a lot. The growth phase gets shorter, and the resting phase gets longer. This leads to thinner, shorter hairs.
The hair follicles also shrink, making finer hairs that fall out easily. The impact of age on hair follicles is complex. Hormonal changes, like the conversion of testosterone to DHT, play a big role in hair loss. DHT makes hair follicles shrink, leading to thinner, shorter hairs.
Typical Age Onset for Different Types of Hair Loss
Different hair loss types start at different ages. Androgenetic alopecia, or male pattern baldness, can start in the late teens or early twenties. The risk grows with age. Other hair loss causes, like medical conditions or stress, can happen at any age.
Distinguishing Age-Related Thinning from Other Causes
Telling age-related hair thinning from other hair loss causes is key for good treatment. The rate of hair loss, the pattern of balding, and overall health help figure out the cause. A healthcare professional or dermatologist can help clarify and suggest treatments.
Knowing the causes of hair loss and how age affects it helps men take care of their hair. Recognizing age-related hair loss signs lets individuals explore treatments to slow or reverse it.
Medical Conditions That Cause Hair Loss
Medical conditions are a big reason for hair loss in men. Different health problems can harm the scalp and hair follicles. This leads to hair falling out.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid problems, like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can make hair fall out. The thyroid gland controls how fast we metabolize. Any imbalance can slow down hair growth. Treatment of thyroid disorders can help manage hair loss.
Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune diseases, like alopecia areata, happen when the immune system attacks hair follicles. This results in hair loss. It can cause patches of hair loss or even total baldness.
Scalp Infections and Diseases
Scalp infections, like ringworm (tinea capitis), and diseases like psoriasis can cause hair loss. These issues cause inflammation and can harm hair follicles if not treated.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional gaps, mainly in iron, zinc, and biotin, can also lead to hair loss. It’s important to eat well to keep hair healthy.
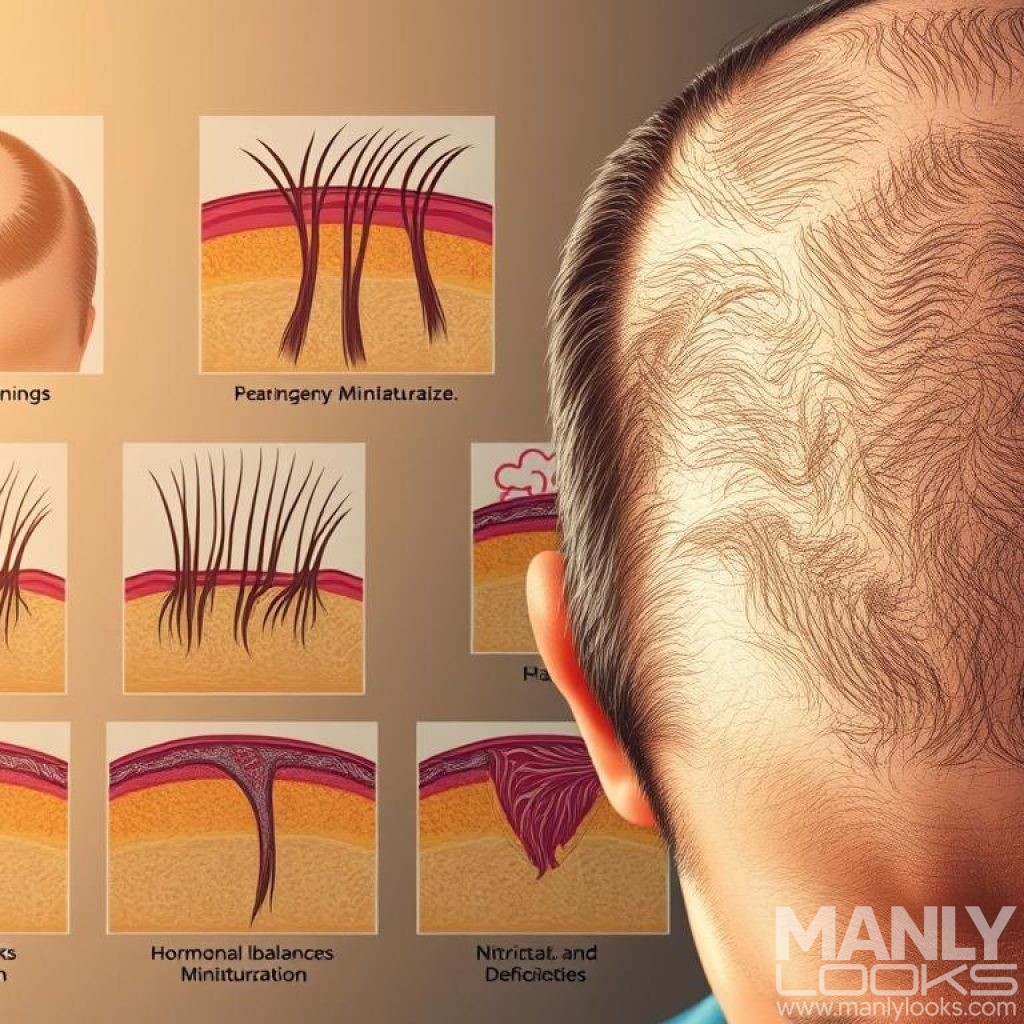
In conclusion, many medical conditions can cause hair loss in men. Knowing about these conditions is key to managing and treating hair loss.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Male Hair Loss
Understanding how daily habits affect hair health is key to fighting male hair loss. Factors like stress, diet, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol play big roles in hair loss in men.

Stress and Hair Loss Connection
Stress is a big factor in hair loss. When we’re stressed, our hair follicles stop growing, causing more hair to fall out. This is called telogen effluvium.
Managing stress is important. Techniques like meditation or yoga can help reduce its impact on hair loss.
Diet and Nutrition Impact
A diet without key nutrients can lead to hair loss. Iron, zinc, and biotin are vital for hair growth. Eating a balanced diet with these nutrients can help stop hair loss.
Smoking, Alcohol, and Other Habits
Smoking and drinking too much can cause hair loss. Smoking harms hair follicles, and alcohol can lead to nutritional deficiencies that harm hair.
Exercise and Its Effects on Hair Health
Exercise is good for overall health, including hair health. It boosts blood flow and reduces stress. But too much exercise can stress the body, leading to hair loss.
Living a healthy lifestyle is essential to prevent or slow hair loss. By managing stress, eating right, avoiding harmful habits, and exercising wisely, men can lower their risk of hair loss.
Medications and Treatments That Can Cause Hair Loss
Certain medications and treatments can cause hair loss in men. This can be upsetting and affect how they feel about themselves. Hair loss, or alopecia, can happen for many reasons, like genetics, hormonal imbalances, and medical conditions. But, some medicines can also cause hair loss.
Common Medications With Hair Loss Side Effects
Several medications have been linked to hair loss in men. These include:
- Antidepressants, like SSRIs
- Beta-blockers and heart medications
- Anticoagulants
- Some anticonvulsants and mood stabilizers
Not everyone taking these medicines will lose their hair. How likely it is can depend on the person and the medicine.
Cancer Treatments and Hair Loss
Cancer treatments, like chemotherapy and radiation, are known to cause hair loss. Chemotherapy targets fast-growing cells, including hair follicles, leading to hair loss all over. Radiation therapy can also cause hair loss, mainly when it’s applied to the scalp.

Temporary vs. Permanent Medication-Induced Hair Loss
The type of hair loss from medicines and treatments can differ. Sometimes, hair loss is temporary and hair grows back after treatment stops or ends. For example, many men lose their hair during chemotherapy, but it usually grows back after treatment.
| Treatment Type | Likelihood of Hair Loss | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | High | Usually reversible |
| Radiation Therapy (Scalp) | High | Can be permanent, depending on dose |
| Certain Medications (e.g., antidepressants, beta-blockers) | Variable | Usually reversible upon stopping medication |
Knowing the side effects of medicines and treatments can help men make better health choices. It can also help them find other options if hair loss is a big worry.
Different Types of Hair Loss Patterns in Men
It’s important to know about the different hair loss patterns in men. Hair loss, or alopecia, can show up in many ways. It depends on genetics, age, and health.
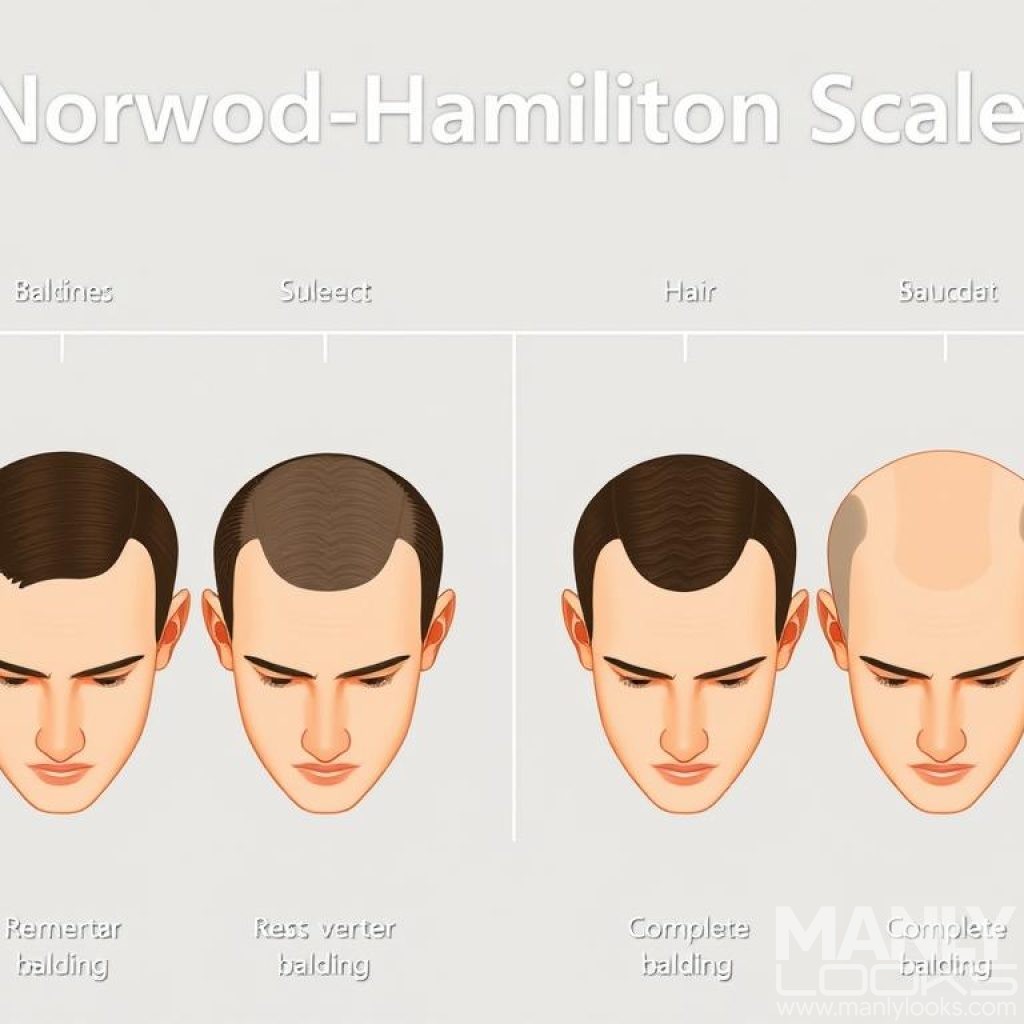
The Norwood-Hamilton Scale
The Norwood-Hamilton Scale helps classify male pattern baldness. It has seven stages, from a little hair loss to a lot. Stage I shows just a bit of hair loss. Stage VII means almost all hair is gone, leaving a horseshoe shape around the head.
Diffuse Thinning vs. Receding Hairline
Men can lose hair in two main ways: diffuse thinning and a receding hairline. Diffuse thinning means hair gets thinner all over. A receding hairline makes the hair thin around the temples, forming an ‘M’ shape.
As
“Hair loss is a common concern for many men, affecting not just their appearance but also their self-esteem and confidence.”
Knowing how you lose hair helps pick the best treatment.
Unusual Hair Loss Patterns and What They Mean
Some men have hair loss that’s not common, like alopecia areata or traction alopecia. These need special treatments.
By figuring out the exact hair loss pattern, men can find the best treatment. This could be medicine, surgery, or changing their lifestyle.
Diagnosing the Cause of Hair Loss
To tackle hair loss, finding its cause is key. Doctors use medical history, physical checks, and tests to figure it out.
When to See a Doctor
Seeing a doctor is vital if you’re losing a lot of hair. Early diagnosis helps in finding better treatments. Men should visit a doctor if they see a lot of hair falling out or bald spots.
Common Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Doctors run different tests to find out why hair is falling out. These include:
- Blood tests to check for hormonal imbalances or deficiencies
- Skin biopsies to examine the scalp
- Pull tests to assess the severity of hair loss
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | What it Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Test | To identify hormonal imbalances | Thyroid function, testosterone levels |
| Skin Biopsy | To examine the scalp condition | Scalp health, presence of diseases |
| Pull Test | To assess hair loss severity | Hair shedding rate |
Working With Dermatologists and Hair Specialists
Dermatologists and hair specialists are vital in diagnosing and treating hair loss. They offer tailored advice and treatment plans based on the diagnosis.

Knowing why men lose their hair and the men hair loss reasons is essential. By consulting specialists and getting the right tests, men can find effective treatments for their hair loss.
Medical Treatments for Male Hair Loss
There are many medical treatments for male hair loss. These options include FDA-approved drugs and new therapies. Each has its own benefits and possible side effects.
FDA-Approved Medications
The FDA has approved two main drugs for male hair loss: finasteride and minoxidil. Finasteride, known as Propecia, stops DHT hormone production. This hormone causes hair loss. Minoxidil, or Rogaine, is applied to the scalp to grow hair and slow loss.
Off-Label Treatment Options
Some treatments are used off-label for hair loss. This means they’re not FDA-approved for this use but might help. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy are examples. They aim to boost hair growth by improving scalp blood flow and using the body’s own platelets.
Emerging Medical Therapies
New treatments for male hair loss are being researched. One promising area is using stem cells to grow new hair follicles. This therapy is experimental but could help restore hair in bald spots.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Men thinking about hair loss treatments should know the possible side effects. Finasteride might cause sexual problems like low libido or erectile dysfunction. Minoxidil can irritate the scalp. It’s important to talk to a doctor about these risks before starting treatment.
Surgical Options for Hair Restoration
Men looking for a fuller head of hair might consider surgery. Hair loss affects many men worldwide, impacting their self-esteem. Surgical options can help those with male pattern baldness or other hair loss issues.
Hair Transplantation Techniques
Hair transplantation moves hair follicles from one part of the body to another. It’s often from the back and sides to the balding areas. There are two main methods: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
FUT takes a strip of hair-bearing skin from the back. It’s then cut into individual follicular units for transplant. FUE, by contrast, extracts individual follicular units directly from the donor site using a special tool.
Candidate Selection for Hair Transplantation
Not everyone is a good candidate for hair transplantation. It works best for men with male pattern baldness and enough donor hair. The extent of hair loss, donor hair quality and quantity, and overall health are key factors.
Recovery and Results Timeline
Recovery includes swelling, redness, and scabbing, which go away in a few weeks. The transplanted hair falls out in 1-2 weeks, but the follicles start growing new hair in 3-4 months. Full results take 12-18 months.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
Hair transplantation costs vary based on location, surgeon’s skill, and graft number. It can range from $3,000 to $15,000. Insurance usually doesn’t cover it, as it’s seen as cosmetic.
Men thinking about hair restoration surgery should talk to a dermatologist or hair specialist. They can help find the best treatment for their needs.
The Psychological Impact of Hair Loss in Men
Male hair loss is more than just a physical problem. It also affects a man’s mind and feelings. Losing hair can change how a man sees himself, his confidence, and his mental health.
Body Image and Self-Esteem Issues
Hair loss can make men feel less about themselves. They might see themselves as less attractive or less manly. This can hurt their confidence in both personal and work life.
“The way we look affects how we feel about ourselves, and hair loss can be a significant blow to a man’s self-image.” This shows how important it is to deal with the emotional side of hair loss.
Social and Professional Impacts
Hair loss can also change how men act in social situations and at work. Some men might feel too shy or worried about how they look. This can make them pull back from social events or do worse at their jobs.
- Social anxiety due to perceived changes in appearance
- Professional impacts, such as decreased confidence in the workplace
- Strained personal relationships due to lowered self-esteem
Coping Strategies and Support Resources
But, there are ways for men to handle the emotional side of hair loss. They can talk to experts like therapists or counselors. They can also look into ways to restore their hair.
Embracing Hair Loss as an Option
For some, accepting their hair loss can be a big step. It means they can start to see themselves in a new light. They can focus on who they are beyond their hair.
Embracing hair loss can free men from the pressure to have a certain look. It lets them focus on their overall health and happiness.
Conclusion
Men often wonder what causes their hair loss. This guide has shown that many factors contribute to it. These include genetics, lifestyle, and health issues.
Finding out why men lose hair is key to choosing the right treatment. Options range from medical treatments to lifestyle changes and surgery. Knowing the cause helps men make better choices for their hair.
By learning about hair loss causes and treatments, men can act early. This approach not only helps with hair loss but also boosts their self-confidence. It’s a step towards feeling better about themselves.




